Building a Production-Ready Data Pipeline with Azure (Part 6): Operationalizing the Gold Layer
- Delta Lake
- Gold Layer
- Scheduling
- Data Engineering
Building a Production Ready Data Pipeline with Azure Part 6: Implementing the Gold Layer with Advanced Scheduling and Dependency Management
Series Overview
This is Part 6 of our comprehensive series on building production-ready data pipelines with Azure:
- Part 1: Complete Guide to Medallion Architecture - Foundation of Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers
- Part 2: Unity Catalog Integration - Implementing data governance and catalog
- Part 3: Advanced Unity Catalog Table Management - Deep dive into table optimization
- Part 4: From Mount Points to Unity Catalog - Migration strategies and best practices
- Part 5: Implementing CI/CD for Azure Data Factory - DevOps practices for data pipelines
- Part 6: Gold Layer Implementation (This article) - Advanced scheduling and dependency management
Introduction
After establishing our Bronze and Silver layers, implementing Unity Catalog, and setting up CI/CD pipelines, we now arrive at the crown jewel of our Medallion Architecture the Gold Layer. This layer transforms cleaned, validated data into business-ready insights that power dashboards, reports, and analytics.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how to build a sophisticated Gold Layer that handles complex dependencies, supports flexible scheduling, enables same-day reruns, and maintains SLA compliance all while being resilient and self-healing.
Table of Contents
- Gold Layer Architecture and Design Principles
- Building the Control Framework
- Implementing Advanced Dependency Management
- Flexible Scheduling with CRON Expressions
- Smart Pipeline Execution with Conditional Logic
- Time-Based Refresh Controls and Same-Day Reruns
- Multi-Trigger Strategy for Business Requirements
- Production Monitoring and SLA Management
- Real-World Implementation Example
- Best Practices and Lessons Learned
1. Gold Layer Architecture and Design Principles
The Gold Layer represents the business-facing layer of our data architecture, where technical data transforms into business value. Unlike Bronze (raw data) and Silver (cleaned data), Gold focuses on business logic and user consumption.
Key Characteristics of Gold Layer
# Gold Layer Characteristics
gold_layer = {
"purpose": "Business-ready analytics and reporting",
"consumers": ["Power BI", "Tableau", "Excel", "APIs"],
"transformations": [
"Complex aggregations",
"Business KPI calculations",
"Denormalization for performance",
"Time-series analysis",
"Predictive scoring"
],
"update_patterns": [
"Daily summaries",
"Hourly metrics",
"Real-time dashboards",
"Monthly reports"
]
}
Design Principles
- Business-Driven: Every Gold table serves specific business needs
- Performance-Optimized: Pre-aggregated for fast query response
- Dependency-Aware: Only processes when source data is ready
- Schedule-Flexible: Supports various refresh frequencies
- Self-Documenting: Clear naming and metadata
2. Building the Control Framework
The foundation of our Gold Layer is a robust control framework that manages configurations, dependencies, and processing status.
Gold Configuration Schema
-- Gold Layer Configuration Table
CREATE TABLE ctl.GoldLayerConfig (
GoldConfigId INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
GoldTableName NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
GoldCategory NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- 'aggregation', 'kpi', 'report', 'ml_feature'
GoldPath NVARCHAR(500),
NotebookPath NVARCHAR(500) NOT NULL,
TransformationType NVARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'spark',
RefreshFrequency NVARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- 'daily', 'hourly', 'weekly', 'monthly', 'custom'
RefreshSchedule NVARCHAR(50), -- CRON expression for custom schedules
BusinessOwner NVARCHAR(100),
Description NVARCHAR(500),
SLAHours INT DEFAULT 24,
Priority INT DEFAULT 100,
IsActive BIT DEFAULT 1,
CreatedDate DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE(),
ModifiedDate DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE()
);
-- Gold Dependencies Table
CREATE TABLE ctl.GoldDependencies (
DependencyId INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
GoldConfigId INT NOT NULL,
DependentTableId INT NOT NULL,
DependencyType NVARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'required', -- 'required', 'optional'
MinimumFreshness INT DEFAULT 24, -- Hours
FOREIGN KEY (GoldConfigId) REFERENCES ctl.GoldLayerConfig(GoldConfigId),
FOREIGN KEY (DependentTableId) REFERENCES ctl.Tables(TableId)
);
-- Gold SLA Tracking
CREATE TABLE ctl.GoldSLATracking (
TrackingId INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
GoldConfigId INT NOT NULL,
ProcessingDate DATE NOT NULL,
ProcessingDateTime DATETIME2,
ExpectedTime DATETIME2,
ActualTime DATETIME2,
SLAStatus NVARCHAR(20), -- 'pending', 'met', 'breached'
BreachReason NVARCHAR(500),
RecordsProcessed BIGINT,
ProcessingDurationMinutes INT,
FOREIGN KEY (GoldConfigId) REFERENCES ctl.GoldLayerConfig(GoldConfigId)
);
Implementing the Configuration
-- Example: Configure a daily sales summary Gold table
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldLayerConfig
(GoldTableName, GoldCategory, NotebookPath, RefreshFrequency, BusinessOwner, SLAHours, Priority) VALUES
('daily_sales_summary', 'aggregation', '/Workspace/Gold/sales_summary', 'daily', 'Sales Team', 4, 100);
-- Define dependencies
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldDependencies (GoldConfigId, DependentTableId, DependencyType, MinimumFreshness) SELECT
gc.GoldConfigId,
t.TableId,
'required',
24
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
CROSS JOIN ctl.Tables t
WHERE gc.GoldTableName = 'daily_sales_summary'
AND t.TableName IN ('SalesOrderHeader', 'SalesOrderDetail', 'Customer');
3. Implementing Advanced Dependency Management
One of the most critical aspects of Gold Layer processing is ensuring all dependencies are met before processing begins. Our implementation uses a sophisticated dependency checking mechanism.
The Dependency Check Stored Procedure
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE ctl.sp_CheckGoldReadiness
@ProcessingDate DATE,
@GoldTableName NVARCHAR(100) = NULL,
@ForceRerun BIT = 0
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @CurrentDateTime DATETIME = GETDATE();
DECLARE @DayOfWeek INT = DATEPART(WEEKDAY, @ProcessingDate);
DECLARE @DayOfMonth INT = DAY(@ProcessingDate);
DECLARE @Hour INT = DATEPART(HOUR, @CurrentDateTime);
-- Gold data with dependency analysis
;WITH GoldData AS (
SELECT
gc.GoldConfigId,
gc.GoldTableName,
gc.GoldPath,
gc.NotebookPath,
gc.RefreshFrequency,
gc.RefreshSchedule,
gc.Priority,
-- Count total dependencies
(SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ctl.GoldDependencies WHERE GoldConfigId = gc.GoldConfigId) as TotalDependencies,
-- Count completed dependencies (DISTINCT to avoid duplicates)
(SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT gd.DependentTableId) FROM ctl.GoldDependencies gd
INNER JOIN ctl.ProcessingStatus ps ON ps.TableId = gd.DependentTableId
WHERE gd.GoldConfigId = gc.GoldConfigId
AND ps.Layer = 'Silver'
AND ps.ProcessingDate = @ProcessingDate
AND ps.Status = 'Success') as CompletedDependencies,
-- Schedule evaluation
CASE
WHEN @ForceRerun = 1 THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshFrequency = 'daily' THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshFrequency = 'weekly' AND @DayOfWeek = 2 THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshFrequency = 'monthly' AND @DayOfMonth = 1 THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshFrequency = 'hourly' THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshFrequency = 'custom' AND gc.RefreshSchedule IS NOT NULL THEN
CASE
-- Parse CRON-like expressions
WHEN gc.RefreshSchedule LIKE '0 */%% * * *'
AND @Hour % CAST(SUBSTRING(gc.RefreshSchedule, 5, CHARINDEX(' ', gc.RefreshSchedule, 5) - 5) AS INT) = 0 THEN 1
WHEN gc.RefreshSchedule LIKE '0 [0-9]% * * *'
AND @Hour = CAST(SUBSTRING(gc.RefreshSchedule, 3, CHARINDEX(' ', gc.RefreshSchedule, 3) - 3) AS INT) THEN 1
ELSE 0
END
ELSE 0
END as ShouldRun
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
WHERE gc.IsActive = 1
AND (@GoldTableName IS NULL OR gc.GoldTableName = @GoldTableName)
) SELECT
GoldConfigId,
GoldTableName,
GoldPath,
NotebookPath,
RefreshFrequency,
RefreshSchedule,
Priority,
TotalDependencies,
CompletedDependencies,
CASE
WHEN TotalDependencies = 0 THEN 'No Dependencies'
WHEN TotalDependencies = CompletedDependencies THEN 'All Dependencies Met'
ELSE 'Waiting for Dependencies'
END as DependencyStatus
FROM GoldData
WHERE
ShouldRun = 1
AND TotalDependencies = CompletedDependencies
-- Time-based duplicate prevention (60-minute window) AND (
@ForceRerun = 1
OR NOT EXISTS (
SELECT 1 FROM ctl.ProcessingStatus ps
WHERE ps.TableId = GoldData.GoldConfigId
AND ps.Layer = 'Gold'
AND ps.ProcessingDate = @ProcessingDate
AND ps.Status = 'Success'
AND ps.EndTime IS NOT NULL
AND DATEDIFF(MINUTE, ps.EndTime, @CurrentDateTime) < 60
)
) ORDER BY Priority, GoldConfigId;
END
GO
Key Features of Dependency Management
- Distinct Counting: Prevents duplicate dependency counts
- Freshness Check: Ensures Silver data is recent enough
- Partial Dependencies: Supports optional dependencies
- Priority-Based Execution: Processes critical tables first
4. Flexible Scheduling with CRON Expressions
Our Gold Layer supports various scheduling patterns through a combination of predefined frequencies and CRON expressions.
Understanding CRON Expressions
# CRON Expression Format
# ┌───────────── minute (0-59)
# │ ┌─────────── hour (0-23)
# │ │ ┌───────── day of month (1-31)
# │ │ │ ┌─────── month (1-12)
# │ │ │ │ ┌───── day of week (0-7, 0 and 7 = Sunday)
# │ │ │ │ │
# * * * * *
# Examples:
0 2 * * * # Daily at 2 AM
0 */4 * * * # Every 4 hours
0 9 * * 1 # Every Monday at 9 AM
0 0 1 * * # First day of every month
0 8,12,16 * * * # At 8 AM, 12 PM, and 4 PM daily
Implementing Custom Schedules
-- Example: Different schedules for different business needs
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldLayerConfig (GoldTableName, RefreshFrequency, RefreshSchedule, NotebookPath) VALUES
-- Standard daily report
('daily_revenue_summary', 'daily', NULL, '/Workspace/Gold/revenue_summary'),
-- Hourly operational dashboard
('hourly_operations_kpi', 'hourly', NULL, '/Workspace/Gold/operations_kpi'),
-- Weekly executive report (Mondays only)
('weekly_executive_dashboard', 'weekly', NULL, '/Workspace/Gold/executive_dashboard'),
-- Custom: Three times a day (6 AM, 2 PM, 10 PM)
('intraday_sales_metrics', 'custom', '0 6,14,22 * * *', '/Workspace/Gold/sales_metrics'),
-- Custom: Every 4 hours during business hours
('business_hours_inventory', 'custom', '0 8-20/4 * * 1-5', '/Workspace/Gold/inventory');
5. Smart Pipeline Execution with Conditional Logic
The Gold Processing Pipeline implements intelligent execution logic that only processes tables when necessary.
Azure Data Factory Pipeline Structure
{
"name": "PL_Gold_Processing",
"properties": {
"activities": [
{
"name": "Get Ready Gold Tables",
"type": "Lookup",
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "AzureSqlSource",
"sqlReaderStoredProcedureName": "ctl.sp_CheckGoldReadiness",
"storedProcedureParameters": {
"ProcessingDate": "@pipeline().parameters.ProcessingDate",
"GoldTableName": "@pipeline().parameters.GoldTableName",
"ForceRerun": "@pipeline().parameters.ForceRerun"
}
},
"dataset": {
"referenceName": "DS_Control_Database",
"type": "DatasetReference"
},
"firstRowOnly": false
}
},
{
"name": "ForEach Gold Table",
"type": "ForEach",
"dependsOn": [{"activity": "Get Ready Gold Tables", "dependencyConditions": ["Succeeded"]}],
"typeProperties": {
"items": "@if(greater(activity('Get Ready Gold Tables').output.count,0), activity('Get Ready Gold Tables').output.value, json('[]'))",
"activities": [
{
"name": "Execute Gold Notebook",
"type": "DatabricksNotebook",
"typeProperties": {
"notebookPath": "@{item().NotebookPath}",
"baseParameters": {
"processing_date": "@pipeline().parameters.ProcessingDate",
"gold_config_id": "@{string(item().GoldConfigId)}",
"gold_table_name": "@{item().GoldTableName}"
}
}
}
]
}
}
],
"parameters": {
"ProcessingDate": {"type": "string"},
"GoldTableName": {"type": "string", "defaultValue": ""},
"ForceRerun": {"type": "bool", "defaultValue": false}
}
}
}
Databricks Notebook Example
# Gold Layer Notebook Template
# Parameters
dbutils.widgets.text("processing_date", "") dbutils.widgets.text("gold_config_id", "") dbutils.widgets.text("gold_table_name", "")
processing_date = dbutils.widgets.get("processing_date") gold_config_id = dbutils.widgets.get("gold_config_id") gold_table_name = dbutils.widgets.get("gold_table_name")
print(f"Processing Gold Table: {gold_table_name} for date: {processing_date}")
# Import required libraries
from pyspark.sql import functions as F
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import logging
# Set up logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Example: Daily Sales Summary
def create_daily_sales_summary():
"""Create aggregated sales summary from Silver layer tables"""
# Read Silver layer tables
sales_orders = spark.table("silver_prod.sales_salesorderheader") \
.filter(F.col("_processing_date") == processing_date) \
.filter(F.col("_is_deleted") == False) sales_details = spark.table("silver_prod.sales_salesorderdetail") \
.filter(F.col("_processing_date") == processing_date) \
.filter(F.col("_is_deleted") == False) customers = spark.table("silver_prod.sales_customer") \
.filter(F.col("_processing_date") == processing_date) \
.filter(F.col("_is_deleted") == False)
# Perform aggregations
daily_summary = sales_orders \
.join(sales_details, "SalesOrderID") \
.join(customers, "CustomerID") \
.groupBy(
F.date_format("OrderDate", "yyyy-MM-dd").alias("order_date"),
"TerritoryID",
"OnlineOrderFlag"
) \
.agg(
F.countDistinct("SalesOrderID").alias("total_orders"),
F.countDistinct("CustomerID").alias("unique_customers"),
F.sum("SubTotal").alias("subtotal_amount"),
F.sum("TaxAmt").alias("tax_amount"),
F.sum("Freight").alias("freight_amount"),
F.sum("TotalDue").alias("total_revenue"),
F.avg("TotalDue").alias("avg_order_value"),
F.max("TotalDue").alias("max_order_value"),
F.min("TotalDue").alias("min_order_value")
) \
.withColumn("processing_date", F.lit(processing_date)) \
.withColumn("etl_timestamp", F.current_timestamp())
# Write to Gold table
daily_summary.write \
.mode("overwrite") \
.option("overwriteSchema", "true") \
.saveAsTable(f"gold_prod.{gold_table_name}") return daily_summary.count()
# Execute based on table name
try:
if gold_table_name == "daily_sales_summary":
record_count = create_daily_sales_summary()
# Add more Gold table transformations here
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown Gold table: {gold_table_name}")
# Return success
result = {
"status": "SUCCESS",
"table_name": f"gold_prod.{gold_table_name}",
"record_count": record_count,
"processing_date": processing_date
}
logger.info(f" Gold table created successfully: {result}") dbutils.notebook.exit(json.dumps(result)) except Exception as e:
logger.error(f" Error processing Gold table: {str(e)}") raise
6. Time-Based Refresh Controls and Same-Day Reruns
A critical requirement for production systems is the ability to rerun processes within the same day, especially after fixing issues or updating business logic.
Implementing Time-Based Controls
Our solution uses the EndTime field to implement a 60-minute cooldown period, preventing duplicate runs while allowing legitimate reruns:
-- The time-based control logic in sp_CheckGoldReadiness
AND (
@ForceRerun = 1 -- Bypass all checks if ForceRerun is set
OR NOT EXISTS (
SELECT 1 FROM ctl.ProcessingStatus ps
WHERE ps.TableId = GoldData.GoldConfigId
AND ps.Layer = 'Gold'
AND ps.ProcessingDate = @ProcessingDate
AND ps.Status = 'Success'
AND ps.EndTime IS NOT NULL
AND DATEDIFF(MINUTE, ps.EndTime, @CurrentDateTime) < 60 -- 60-minute window
)
)
Use Cases for Same-Day Reruns
- Bug Fixes: Business logic corrections requiring immediate reprocessing
- Data Corrections: When Silver layer data is corrected
- SLA Recovery: Meeting deadlines after initial failures
- Testing: Development and UAT environments
Manual Rerun Strategies
-- Strategy 1: Use ForceRerun parameter
EXEC ctl.sp_CheckGoldReadiness
@ProcessingDate = '2025-01-13',
@GoldTableName = 'daily_sales_summary',
@ForceRerun = 1;
-- Strategy 2: Clear success record (use with caution) DELETE FROM ctl.ProcessingStatus
WHERE TableId = (SELECT GoldConfigId FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig WHERE GoldTableName = 'daily_sales_summary') AND Layer = 'Gold'
AND ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE) AND Status = 'Success';
-- Strategy 3: Update configuration for immediate run
UPDATE ctl.GoldLayerConfig
SET RefreshFrequency = 'hourly'
WHERE GoldTableName = 'critical_kpi_dashboard';
7. Multi-Trigger Strategy for Business Requirements
Different business requirements demand different execution schedules. Our implementation supports multiple triggers working in harmony.
Trigger Architecture
// EST_Gold_Processing_Morning.json - For early morning reports
{
"name": "EST_Gold_Processing_Morning",
"properties": {
"runtimeState": "Started",
"pipelines": [{
"pipelineReference": {"referenceName": "PL_Gold_Processing"},
"parameters": {
"ProcessingDate": "@formatDateTime(trigger().scheduledTime, 'yyyy-MM-dd')",
"GoldTableName": "",
"ForceRerun": false
}
}],
"type": "ScheduleTrigger",
"typeProperties": {
"recurrence": {
"frequency": "Day",
"interval": 1,
"startTime": "2024-01-01T06:00:00",
"timeZone": "Eastern Standard Time",
"schedule": {"hours": [6], "minutes": [0]}
}
}
}
}
// EST_Gold_Processing_Hourly.json - For real-time dashboards
{
"name": "EST_Gold_Processing_Hourly",
"properties": {
"runtimeState": "Started",
"pipelines": [{
"pipelineReference": {"referenceName": "PL_Gold_Processing"}
}],
"type": "ScheduleTrigger",
"typeProperties": {
"recurrence": {
"frequency": "Hour",
"interval": 1,
"timeZone": "Eastern Standard Time"
}
}
}
}
Trigger Strategy Matrix
TriggerScheduleUse CaseGold TablesMorning6 AM ESTExecutive dashboardsDaily summaries, KPIsAfternoon2 PM ESTMid-day updatesOperational metricsEvening10 PM ESTEnd-of-day reportsFinancial summariesHourlyEvery hourReal-time monitoringLive dashboards
How Multiple Triggers Work Together
Single Daily Trigger (2 AM)
↓
Runs PL_Gold_Processing
↓
sp_CheckGoldReadiness evaluates EACH Gold table:
├── daily_sales_summary → RefreshFrequency='daily' → ✓ Process
├── hourly_inventory → RefreshFrequency='hourly' → ✓ Process
├── weekly_report → RefreshFrequency='weekly' → Check day of week
└── monthly_finance → RefreshFrequency='monthly' → Check day of month
8. Production Monitoring and SLA Management
SLA Tracking Implementation
-- SLA Monitoring Dashboard Query
WITH SLAMetrics AS (
SELECT
gc.GoldTableName,
gc.BusinessOwner,
gc.SLAHours,
gst.ProcessingDate,
gst.ExpectedTime,
gst.ActualTime,
gst.SLAStatus,
gst.ProcessingDurationMinutes,
CASE
WHEN gst.SLAStatus = 'breached' THEN
DATEDIFF(MINUTE, gst.ExpectedTime, gst.ActualTime) ELSE 0
END as BreachMinutes
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
LEFT JOIN ctl.GoldSLATracking gst ON gc.GoldConfigId = gst.GoldConfigId
WHERE gst.ProcessingDate >= DATEADD(DAY, -7, GETDATE())
) SELECT
GoldTableName,
BusinessOwner,
COUNT(*) as TotalRuns,
SUM(CASE WHEN SLAStatus = 'met' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as SLAMet,
SUM(CASE WHEN SLAStatus = 'breached' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) as SLABreached,
AVG(ProcessingDurationMinutes) as AvgDurationMinutes,
MAX(BreachMinutes) as MaxBreachMinutes,
CAST(100.0 * SUM(CASE WHEN SLAStatus = 'met' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) / COUNT(*) AS DECIMAL(5,2)) as SLACompliancePercent
FROM SLAMetrics
GROUP BY GoldTableName, BusinessOwner
ORDER BY SLACompliancePercent;
Health Check Procedures
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE ctl.sp_GoldHealthCheck
AS
BEGIN
-- Overall Gold Layer health
SELECT
COUNT(DISTINCT gc.GoldConfigId) as TotalGoldTables,
COUNT(DISTINCT CASE WHEN gc.IsActive = 1 THEN gc.GoldConfigId END) as ActiveGoldTables,
COUNT(DISTINCT CASE WHEN ps.Status = 'Success' AND ps.ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE) THEN ps.TableId END) as ProcessedToday,
COUNT(DISTINCT CASE WHEN ps.Status = 'Failed' AND ps.ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE) THEN ps.TableId END) as FailedToday,
COUNT(DISTINCT CASE WHEN gst.SLAStatus = 'breached' AND gst.ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE) THEN gst.GoldConfigId END) as SLABreachedToday
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
LEFT JOIN ctl.ProcessingStatus ps ON gc.GoldConfigId = ps.TableId AND ps.Layer = 'Gold'
LEFT JOIN ctl.GoldSLATracking gst ON gc.GoldConfigId = gst.GoldConfigId;
-- Failed Gold tables requiring attention
SELECT
gc.GoldTableName,
gc.BusinessOwner,
ps.ProcessingDate,
ps.ErrorMessage,
ps.StartTime,
gc.NotebookPath
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
INNER JOIN ctl.ProcessingStatus ps ON gc.GoldConfigId = ps.TableId
WHERE ps.Layer = 'Gold'
AND ps.Status = 'Failed'
AND ps.ProcessingDate >= DATEADD(DAY, -1, GETDATE()) ORDER BY ps.StartTime DESC;
END
GO
9. Real-World Implementation Example
Let’s walk through a complete example of implementing a Gold Layer table for a retail analytics scenario.
Business Requirement
The sales team needs a daily dashboard showing:
- Revenue by territory and product category
- Customer acquisition metrics
- Inventory turnover rates
- Sales performance vs. targets
Implementation Steps
-- 1. Configure the Gold table
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldLayerConfig
(GoldTableName, GoldCategory, NotebookPath, RefreshFrequency, BusinessOwner, Description, SLAHours, Priority) VALUES
('daily_sales_dashboard', 'kpi', '/Workspace/Gold/sales_dashboard', 'daily', 'Sales Analytics Team',
'Comprehensive daily sales metrics for executive dashboard', 6, 90);
-- 2. Define dependencies
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldDependencies (GoldConfigId, DependentTableId) SELECT
(SELECT GoldConfigId FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig WHERE GoldTableName = 'daily_sales_dashboard'),
TableId
FROM ctl.Tables
WHERE SchemaName = 'Sales'
AND TableName IN ('Customer', 'SalesOrderHeader', 'SalesOrderDetail', 'Product', 'SalesTerritory');
-- 3. Create Databricks notebook (partial code)
"""
# Daily Sales Dashboard Gold Table
# This notebook creates comprehensive sales metrics for business users
# Read Silver tables with optimization
sales_df = spark.read.table("silver_prod.sales_salesorderheader") \
.filter(col("_processing_date") == processing_date) \
.filter(col("_is_deleted") == False) \
.cache() # Cache for reuse
# Complex business logic
sales_metrics = sales_df \
.join(territory_df, "TerritoryID") \
.join(product_df, "ProductID") \
.groupBy("TerritoryName", "ProductCategory", "OrderDate") \
.agg(
# Revenue metrics
sum("TotalDue").alias("total_revenue"),
count("SalesOrderID").alias("order_count"),
countDistinct("CustomerID").alias("unique_customers"),
# Performance metrics
avg("TotalDue").alias("avg_order_value"),
stddev("TotalDue").alias("revenue_volatility"),
# Time-based metrics
sum(when(hour("OrderDate").between(9, 17), col("TotalDue"))).alias("business_hours_revenue"),
sum(when(hour("OrderDate") >= 18, col("TotalDue"))).alias("after_hours_revenue")
) \
.withColumn("revenue_per_customer", col("total_revenue") / col("unique_customers")) \
.withColumn("is_weekend", when(dayofweek("OrderDate").isin(1, 7), 1).otherwise(0))
# Add YoY comparison
last_year_metrics = calculate_last_year_metrics(processing_date) final_metrics = sales_metrics.join(
last_year_metrics,
["TerritoryName", "ProductCategory"],
"left"
).withColumn("yoy_growth",
((col("total_revenue") - col("last_year_revenue")) / col("last_year_revenue") * 100)
)
# Write with optimization
final_metrics.coalesce(10) \
.write \
.mode("overwrite") \
.option("overwriteSchema", "true") \
.partitionBy("OrderDate") \
.saveAsTable("gold_prod.daily_sales_dashboard")
"""
Monitoring the Implementation
-- Check processing history
SELECT
ps.ProcessingDate,
ps.StartTime,
ps.EndTime,
ps.Status,
ps.RecordsProcessed,
DATEDIFF(MINUTE, ps.StartTime, ps.EndTime) as DurationMinutes,
gst.SLAStatus
FROM ctl.ProcessingStatus ps
LEFT JOIN ctl.GoldSLATracking gst ON ps.TableId = gst.GoldConfigId
AND ps.ProcessingDate = gst.ProcessingDate
WHERE ps.TableId = (SELECT GoldConfigId FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig WHERE GoldTableName = 'daily_sales_dashboard') AND ps.Layer = 'Gold'
ORDER BY ps.ProcessingDate DESC;
10. Best Practices and Lessons Learned
1. Design for Reusability
# Create reusable transformation functions
def calculate_revenue_metrics(df, group_by_columns):
"""Reusable function for revenue calculations"""
return df.groupBy(group_by_columns).agg(
F.sum("TotalDue").alias("total_revenue"),
F.count("SalesOrderID").alias("order_count"),
F.avg("TotalDue").alias("avg_order_value")
)
# Use across multiple Gold tables
territory_metrics = calculate_revenue_metrics(sales_df, ["TerritoryID"]) product_metrics = calculate_revenue_metrics(sales_df, ["ProductID"]) time_metrics = calculate_revenue_metrics(sales_df, [F.date_trunc("hour", "OrderDate")])
2. Implement Incremental Processing
# For large datasets, implement incremental processing
def process_incremental_gold(table_name, processing_date, lookback_days=7):
"""Process only recent data for efficiency"""
# Read existing Gold table
existing_df = spark.table(f"gold_prod.{table_name}")
# Get max date in existing data
max_date = existing_df.agg(F.max("order_date")).collect()[0][0]
# Process only new data
new_data = create_gold_metrics(
start_date=max_date + timedelta(days=1),
end_date=processing_date
)
# Merge with existing data
merged_df = existing_df.filter(
F.col("order_date") < F.date_sub(F.current_date(), lookback_days)
).union(new_data)
# Optimize and write
merged_df.coalesce(50) \
.write \
.mode("overwrite") \
.saveAsTable(f"gold_prod.{table_name}")
3. Error Handling and Recovery
-- Implement automatic retry logic
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE ctl.sp_RetryFailedGoldTables
@MaxRetries INT = 3
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @GoldConfigId INT, @RetryCount INT;
DECLARE retry_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT DISTINCT gc.GoldConfigId
FROM ctl.GoldLayerConfig gc
INNER JOIN ctl.ProcessingStatus ps ON gc.GoldConfigId = ps.TableId
WHERE ps.Layer = 'Gold'
AND ps.Status = 'Failed'
AND ps.ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE) AND ps.RetryCount < @MaxRetries;
OPEN retry_cursor;
FETCH NEXT FROM retry_cursor INTO @GoldConfigId;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Trigger retry through ADF API
EXEC ctl.sp_TriggerGoldPipeline @GoldConfigId = @GoldConfigId;
-- Update retry count
UPDATE ctl.ProcessingStatus
SET RetryCount = ISNULL(RetryCount, 0) + 1
WHERE TableId = @GoldConfigId
AND Layer = 'Gold'
AND ProcessingDate = CAST(GETDATE() AS DATE);
FETCH NEXT FROM retry_cursor INTO @GoldConfigId;
END
CLOSE retry_cursor;
DEALLOCATE retry_cursor;
END
4. Performance Optimization
# Optimize Gold table queries
def optimize_gold_table(table_name):
"""Apply optimizations to Gold tables"""
# Z-order optimization for common query patterns
spark.sql(f"""
OPTIMIZE gold_prod.{table_name}
ZORDER BY (order_date, territory_id, product_category)
""")
# Compute statistics
spark.sql(f"ANALYZE TABLE gold_prod.{table_name} COMPUTE STATISTICS")
# Create materialized views for common aggregations
spark.sql(f"""
CREATE OR REPLACE MATERIALIZED VIEW gold_prod.mv_{table_name}_daily
AS SELECT
order_date,
SUM(total_revenue) as daily_revenue,
SUM(order_count) as daily_orders
FROM gold_prod.{table_name}
GROUP BY order_date
""")
5. Documentation and Lineage
-- Maintain comprehensive documentation
CREATE TABLE ctl.GoldLineage (
LineageId INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
GoldTableName NVARCHAR(100),
SourceTable NVARCHAR(100),
SourceLayer NVARCHAR(20),
TransformationLogic NVARCHAR(MAX),
BusinessRules NVARCHAR(MAX),
CreatedDate DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE()
);
-- Document transformations
INSERT INTO ctl.GoldLineage (GoldTableName, SourceTable, SourceLayer, TransformationLogic, BusinessRules) VALUES
('daily_sales_dashboard', 'sales_salesorderheader', 'Silver',
'JOIN with territory and product tables, aggregate by date and territory',
'Revenue includes tax and freight, exclude cancelled orders, YoY comparison uses same day last year');
Conclusion
The Gold Layer represents the culmination of our data pipeline journey, transforming raw data into actionable business insights. By implementing robust dependency management, flexible scheduling, and intelligent processing logic, we’ve created a system that:
- Adapts to changing business requirements through configuration
- Scales with data volume through optimized processing
- Recovers from failures automatically
- Meets SLA requirements consistently
- Enables self-service analytics for business users
The combination of Azure Data Factory’s orchestration capabilities, Databricks’ processing power, and our sophisticated control framework creates a production-ready Gold Layer that serves as the foundation for data-driven decision making.
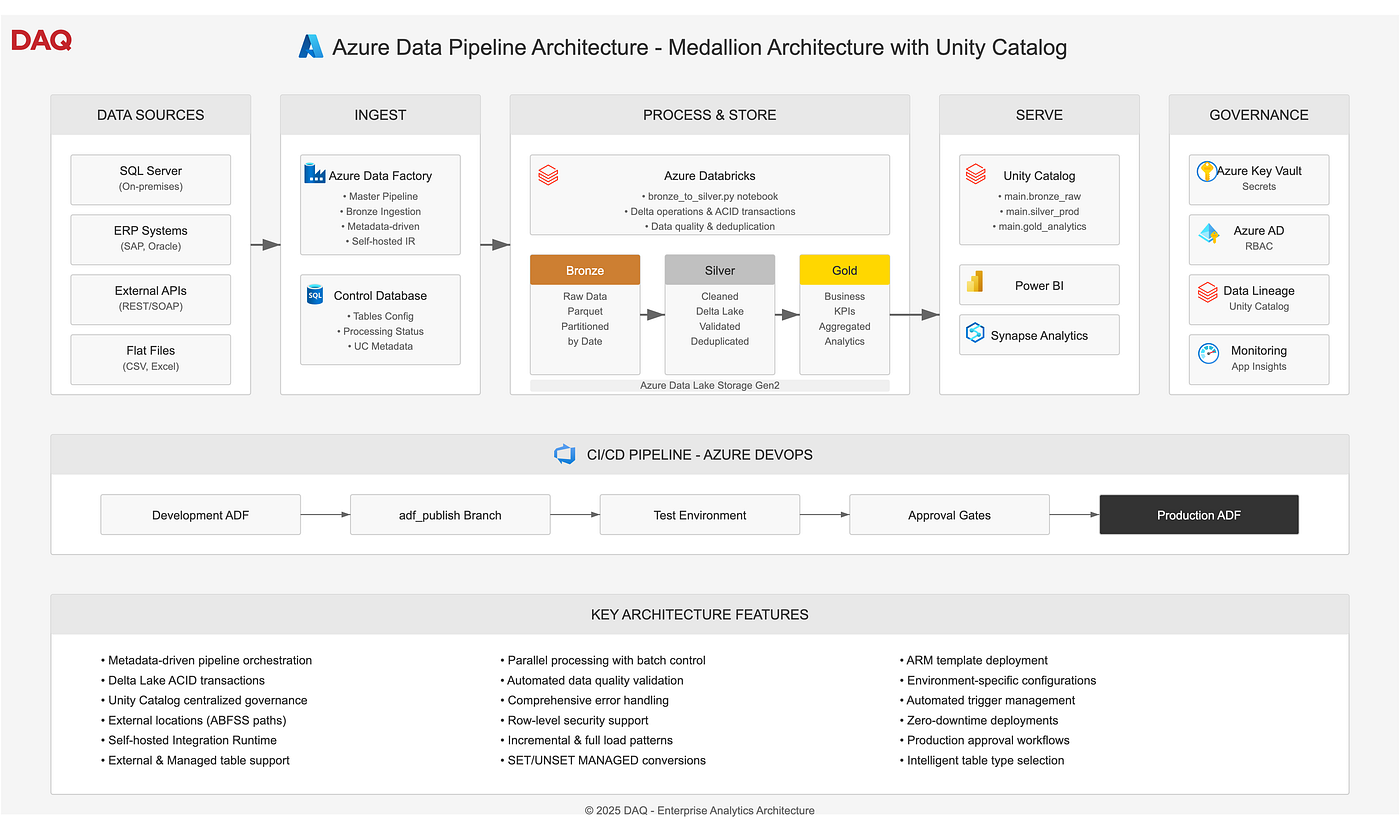
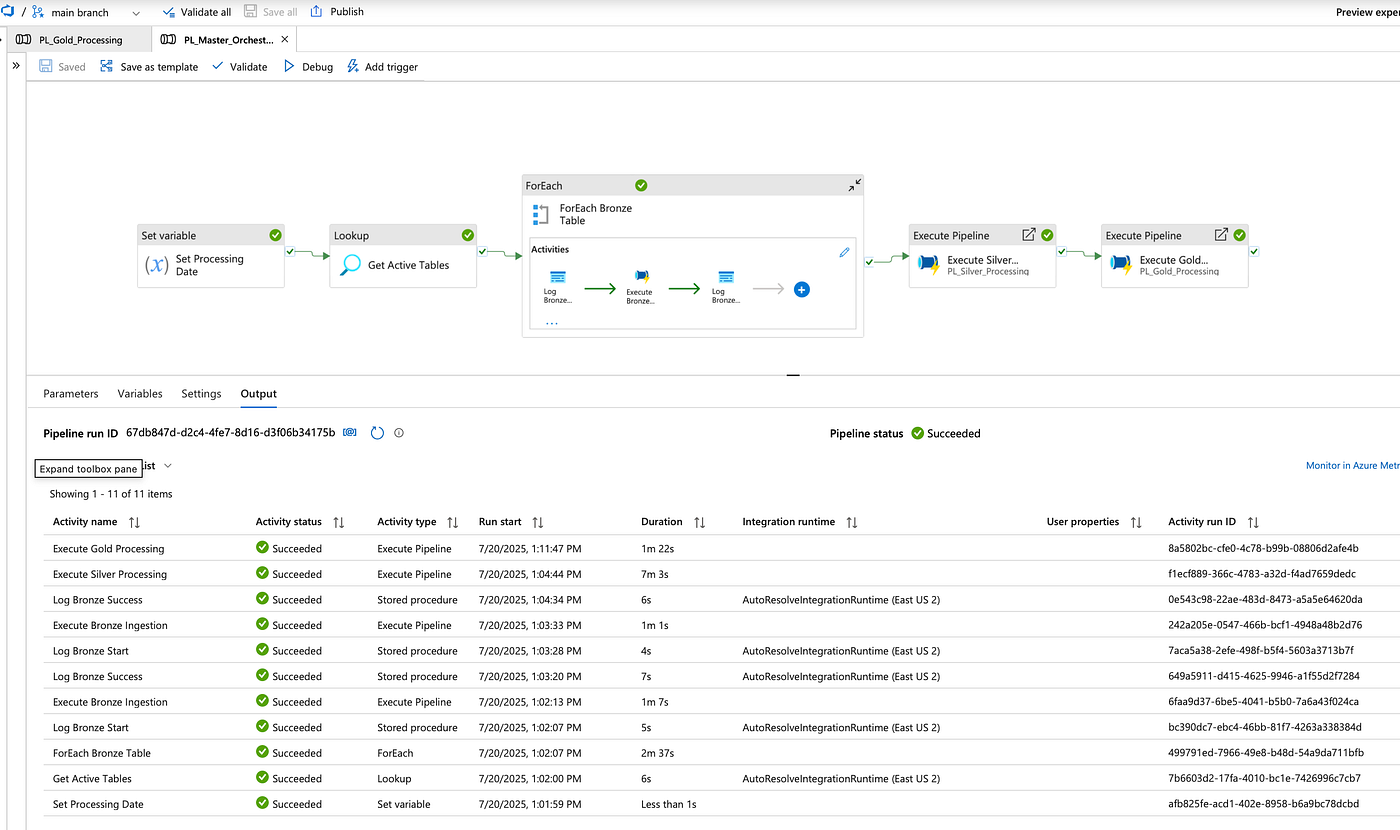
Pipeline Overview:
Have questions or want to share your Gold Layer implementation experiences? Leave a comment below or connect with me on LinkedIn.
#Azure #DataEngineering #Databricks #DataFactory #GoldLayer #Analytics #MedallionArchitecture #BigData #CloudComputing #DataPipeline